- Real-Time Graphics |
- Rendering |
- Animation |
- Geometric Modeling |
- Scientific Visualization |
- Software System

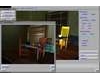
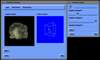
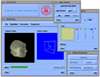
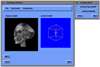
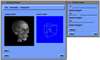
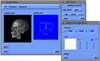
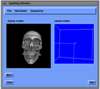
- Mobile Collaborative Medical Display System

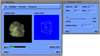
- Photo-Realistic Rendering System
- A Photo-Realistic Rendering System for Physically-Simulated Liquids

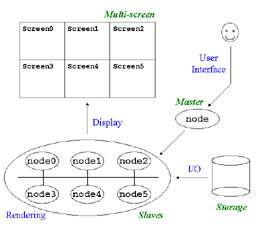
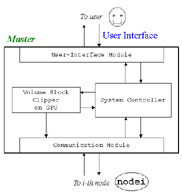
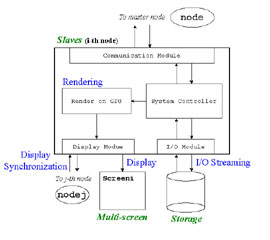
- Construction of High-Performance Display System
- SGVN (SoGang Volume Navigation) A Distributed/Parallel Volume Visualization System on PC/Workstation Clusters

- SGRT (SoGang Rendering Toolkit) : an Advanced Rendering System
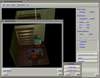
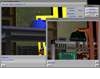
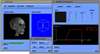
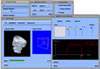
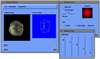
- SGVR (SoGang Volume Rendering) : a Collaborative Volume Visualization System
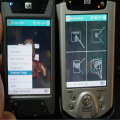
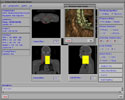
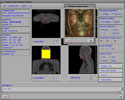
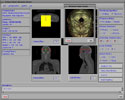
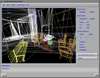
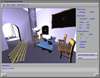
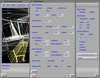
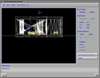
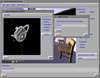
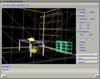
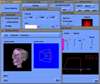
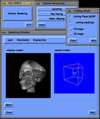
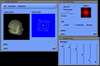
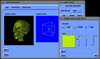
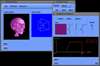
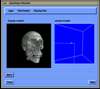
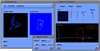
Because of recent advances in wireless communication technologies, the world of mobile computing is flourishing with a variety of applications. In this study, we present an integrated architecture for a personal digital assistant~(PDA)-based mobile medical display system that supports collaborative work between remote users. We aim to develop a system that enables users in different regions to share a working environment for collaborative visualization with the potential for exploring huge medical datasets. Our system consists of three major components: mobile client, gateway, and parallel rendering server. The mobile client serves as a front end and enables users to choose the visualization and control parameters interactively and cooperatively. The gateway handles requests and responses between mobile clients and the rendering server for efficient communication. Through the gateway, it is possible to share working environments between users, allowing them to work together in computer supported cooperative work~(CSCW) mode. Finally, the parallel rendering server is responsible for performing heavy visualization tasks. Our experience indicates that some features currently available to our mobile clients for collaborative scientific visualization are limited due to the poor performance of mobile devices and the low bandwidth of wireless connections. However, as mobile devices and wireless network systems are experiencing considerable elevation in their capabilities, we believe that our methodology will be utilized effectively in building quite responsive, useful mobile collaborative medical systems in the very near future.
- S. Park, W. Kim, and I. Ihm, "Mobile Collaborative Medical Display System," Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, Vol. 89, No. 3, pp. 248-260, March 2008.
- Example 1 [mov1a.avi]
- Example 2 [mov1b.avi]

- 극사실 렌더링을 위한 렌더링 코어 기술 개발
- 상용 CG 소프트웨어 호환 렌더링 시스템 개발
- 실제 3D 애니메이션 제작 과정에 활용 가능한 렌더링 소프트웨어 및 플러그인 개발
- 2006년 5월 ~ 2007년 2월
- 과제명: 포톤 매핑 컴포넌트 개발
- 지원 기관: (주) 디지아트프로덕션
- 지원 내역: 소프트웨어 개발 용역
- 2007년 3월 ~ 2010년 2월
- 과제명: 극사실적 렌더링을 위한 확장 콤포넌트 개발
- 지원 기관: 정보통신부 및 한국전자통신연구원(ETRI)
- 지원 내역: 정보통신 선도기반기술개발사업 공동연구기관

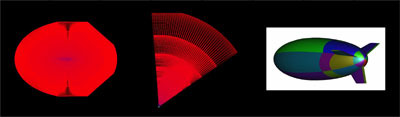
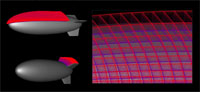
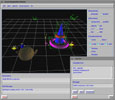
We have been developing a photon mapping-based Monte Carlo ray tracer, aimed at visualizing physically-simulated liquids. This software is specialized for effectively generating photo-realistic rendering images from liquid datasets, in signed distance form, that are frequently produced as a result of physically-based fluid simulation. While this work aims to create a rendering toolkit suitable for 3D animation production, we have also designed the renderer in a way to be flexible enough to function as a test bed for testing/developing new advanced rendering effects for liquids.
- A moving ball: [Rendering], [Photons]
- A falling ball: [sample 1], [sample 2]
- Water inflow (NPR fashion): [sample 1], [sample 2]
- Application to polygonal models: [sample 1], [sample 2]
- Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)

- The tiled display system architecture.
- The software system architecture.
- Raw data. (150 time frames, 211.5GB in total)
- Raw data: grids near surface.
- Temperature display near aircraft's surface (point display).
- Pressure display.
- Point display [7MB] View
- Moving an axis-aligned cutting plane while streaming slowly changing time-varying simulation datasets [14MB] View
- Moving a cutting plane with arbitrary orientations while streaming slowly changing time-varying simulation datasets [16MB] View
- Display of iso-surfaces of pressure field colored with temperature field [5MB] View
- Display of iso-surfaces with different iso-values [26MB] View
- Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI)
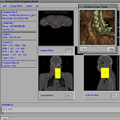
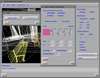
In this work, we have developed a new parallel/distributed ray-casting scheme for very large volume data that can be effectively used in distributed environments. Our method, based on data compression, attempts to enhance the rendering speedups by quickly reconstructing voxel data from local memory rather than expensively fetching them from remote memory spaces. Our compression-based volume rendering scheme minimizes communications between processing elements during rendering computation, hence is very appropriate for both distributed-memory multiprocessors and PC/workstation clusters, where the relatively high communication costs often hinder efficient parallel/distributed processing. We report experimental results on both a Cray T3E and a PC/workstation cluster for the Visible Man dataset.
- C. Bajaj, I. Ihm, S. Park, and D. Song, "Compression-Based Ray Casting of Very Large Volume Data in Distributed Environments," HPC-Asia 2000: The Fourth International Conference/Exhibition on High Performance Computing in Asia-Pacific Region, pp.720-725, Beijing, China, May 2000.
- Examples (SGI version)
- Ministry of Information and Communication

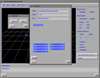
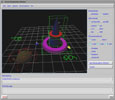
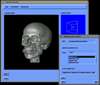
In this work, we have developed an advanced rendering system, called SGRT (SoGang Rendering Toolkit), designed for generating high-quality 3D rendered pictures. It has been developed for about two years in the environment of C/C++, X, Motif, and OpenGL, and amounts to roughly 65,000 lines of source codes. This system is based on the PIXAR RenderMan Interface which allows users to utilize shaders written in the RenderMan Shading Language. In particular, SGRT includes a network toolkit, named MIRAGE, that extends the system to a multi-user rendering system supporting cooperative works.
- K. Im, and I. Ihm, "MIRAGE: a Multi-Server-Based Network Toolkit for Multi-User Collaboration," Journal of KISS (C), Vol. 5, No. 2, pp. 63-78, February 1999.
- R. Lee, K. Paek, H. Han, W. Jung, H. Jung, K. Im, M. Park, and I. Ihm, "Design and Implementation of an Advanced Rendering System," Journal of KISS (C), Vol. 4, No. 5, pp. 633-643, October 1998.
- Example 1
- Example 2
- Multi-user Collaboration
- Ministry of Science and Technology
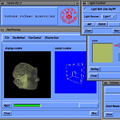
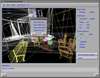
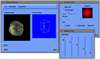
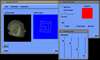
Volume visualization has been increasingly important in computer graphics and other related scientific disciplines ranging from the medical science to the computational fluid mechanics. Many effective visualization methods have been studied and as a result, several volume visualization systems such as Explorer, AVS and VolVis have emerged. SGVR is a new volume visualization system designed for the purpose of utilizing the new computing technologies such as multimedia, high-speed network, and collaborative computing in visualization tasks. It integrates the state-of-the-art visualization techniques and provides a wide range of capabilities for the researchers and practitioners who need volume visualization. Especially it's collaboration and multimedia capabilities enable several users to share and interact with each other for common purpose of visualization on multiple networked workstations. In this development effort, we consider the design concepts and implementation details of our new visualization system, and show how it can be used for a group of people to effectively solve common problems in a collaborative manner.
- K. Paek, and I. Ihm, "SGVR: A Collaborative Volume Visualization System," Journal of KISS (A) , Vol. 24, No. 5, pp. 417-428, May 1997.
- Example
- Systems Engineering Research Institute